Have you met John?
John doesn’t spend a lot of time thinking about the anatomy of his Guitar. He might be more concerned with the feel of the neck, the action of the strings, or the tone of the pickups.
DON’T Be Like John!❌
If you want to really understand how your guitar works, and how to make it work best for you, it’s important to have at least a basic understanding of guitar anatomy.
From the graceful curves of the body to the intricate details of the neck and headstock, every component of a guitar plays a crucial role in shaping its sound and playability.
So, let’s embark on this educational journey and uncover the secrets of guitar anatomy!
Guitar Anatomy Summary
- Guitar anatomy is essential knowledge for beginners.
- Common guitar parts include the body, neck, headstock, and fretboard.
- Electric guitars have additional components such as pickups and potentiometers.
- Acoustic guitars utilize the resonant body for sound projection.
- Understanding guitar anatomy helps in choosing the perfect instrument for your needs.
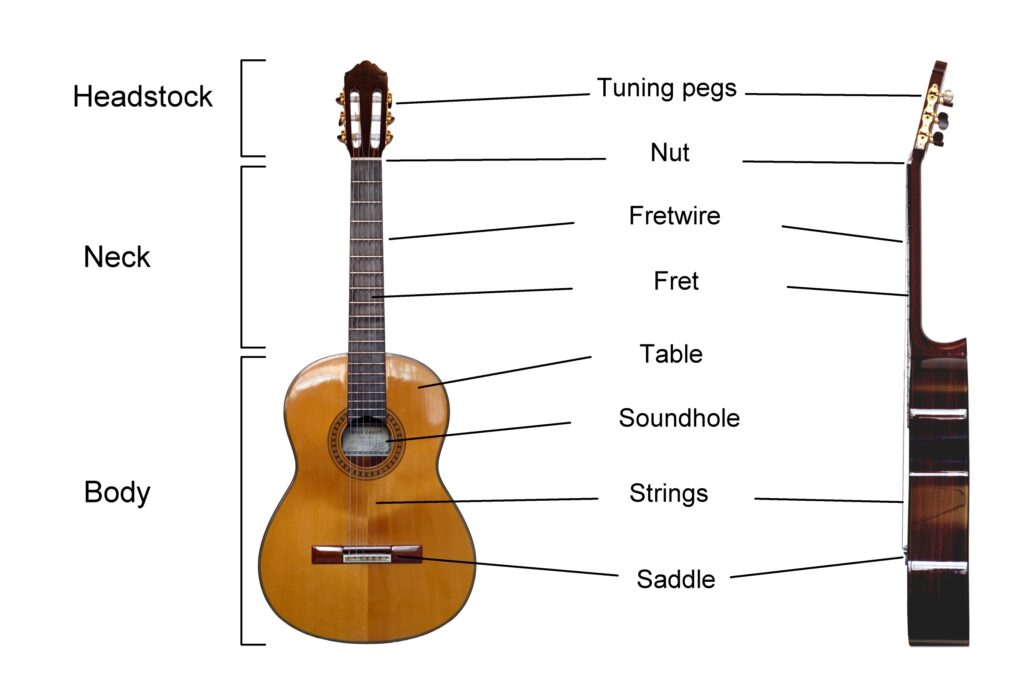
Parts of an Acoustic Guitar
Let’s discuss the various parts of an Acoustic Guitar.
- Headstock
This is the top part of the guitar where the tuning pegs are located. The tuning pegs are used to adjust the tension of the strings by rotating them either clockwise or anti-clockwise which, in turn, changes the pitch of the strings. The strings are named EADBGE in a standard setup. Each letter represents the pitch of the string to which it is tuned. - Nut
The nut is a small component that sits between the headstock and the fretboard of a guitar. Its main function is to evenly space out the strings. Usually, Nuts are made from plastic or bone. - Neck
The neck connects the headstock to the body. It is an important part of the guitar as it contains the Fingerboard – A part with which the guitar player interacts the most. - Fingerboard
The fingerboard is a flat, smooth surface on top of the neck which consists of Frets. Pressing down a string behind a particular fret allows the guitarist to change the pitch of a string’s note. - Body
The body is where the sound is produced and amplified. - Soundhole
The soundhole is a hole in the front of the guitar’s body that allows the sound to be projected and reach our ears. - Bridge
The main purpose of the bridge is to anchor the strings to the body of the guitar. It also helps transfer the vibrations of the strings to the guitar’s top and other parts which is very important for producing Good Pronounced Sound. - Saddle
The saddle is a small strip of material (usually plastic or bone) that sits on top of the bridge and helps keep the strings at the right height above the body. - Pickguard
The pickguard is usually made of plastic that sits on the front of the guitar’s body and protects it from scratches and damage caused by strumming or picking.
By understanding the parts of an acoustic guitar, you’ll not only gain a deeper appreciation for this instrument but also be better equipped to explore and experiment with its unique sound.
Parts of an Electric Guitar
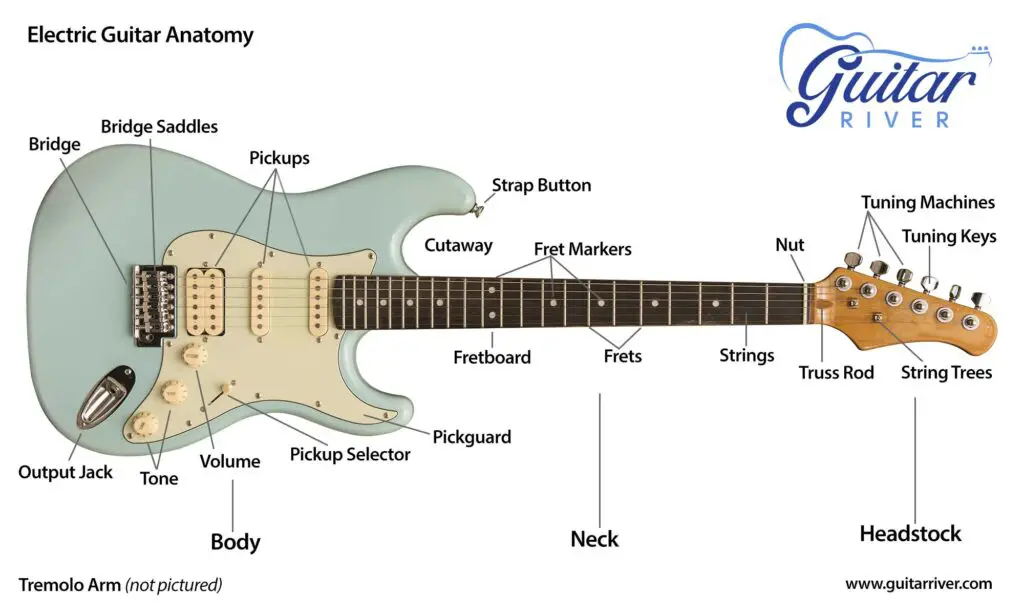
The majority of the components of an Electric Guitar are similar to that of an Acoustic Guitar with a few additions.
As the name suggests, Electric guitars cannot produce the sound acoustically but rather with the help of electronic components embedded in their bodies.
Here’s a breakdown of the anatomy of an electric guitar:
- Headstock
The headstock serves the same purpose as an acoustic guitar. Electric guitars have different headstock shapes. It varies from brand to brand. The most iconic headstock shapes are that of a Fender Stratocaster and a Gibson Les Paul. - Nut
The nut in an electric guitar is made of plastic or bone. It keeps the strings evenly spaced. - Neck
Electric guitar necks are made of woods such as maple, mahogany, or rosewood and have a fretboard. - Fingerboard
The fingerboard consists of Frets which divide the fretboard into different parts. The most common Fingerboard woods are Rosewood and Maple. - Body
The body of an electric guitar is made of solid wood such as mahogany or basswood. Different brands have different shapes of guitar bodies. The most common shape is the Stratocaster. - Pickups
They are electronic devices (a magnet wrapped with thin copper wire windings) placed under the strings on the guitar’s body. They catch the vibrations of the strings and convert them into electrical signals which are then sent to an amplifier. - Bridge
The bridge is a metal component located on the front of the guitar’s body that anchors the strings to the body. It also helps transfer the vibrations of the strings to the guitar’s pickups. - Tremolo
Some guitars have Tremolo systems, and some don’t. Basically, a tremolo allows you to change the pitch of the strings by pressing the tremolo bar. - Volume and Tone Controls
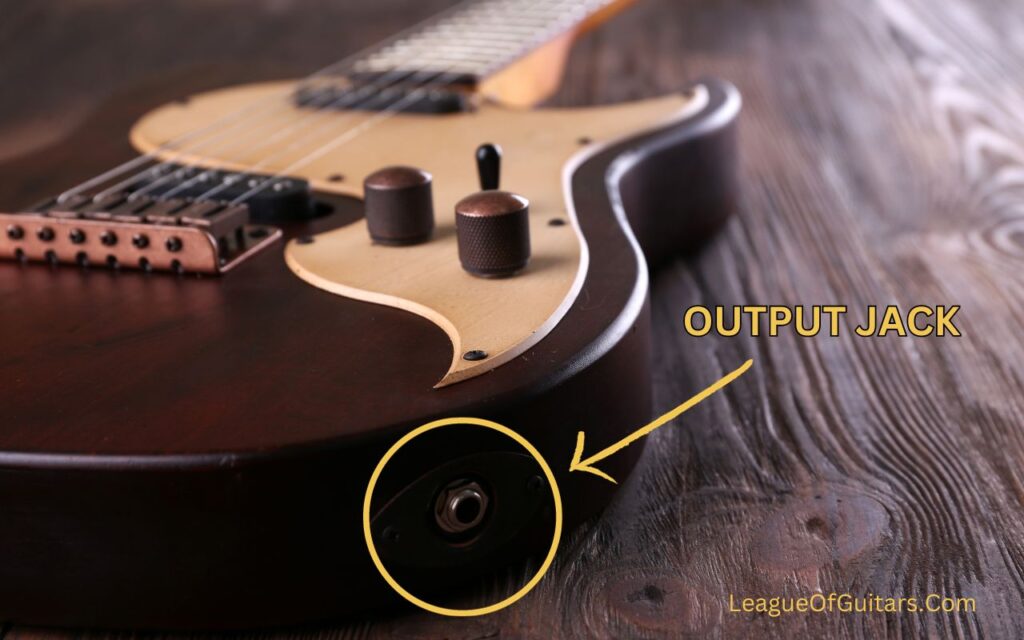
With these knobs, you can adjust the volume and tone of the guitar. - Output Jack
The output jack is a small socket on the guitar’s body where you can insert a 6.35 mm cable connector to connect the guitar to an amplifier.
Let’s talk about the electronic components in more detail, as they are unique to an electric guitar and without them, the guitar can’t transmit the sound to an external amplifier/speaker.
Electric Guitar Pickups
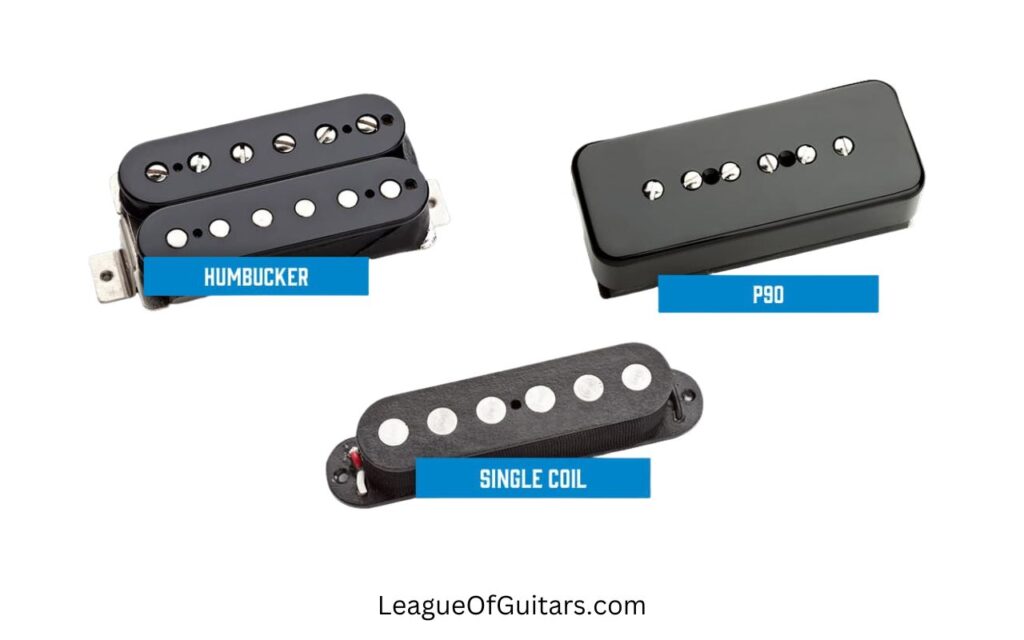

Pickups are magnets wrapped in wire coils that convert the vibrations of the guitar strings into electrical signals. The signals are then amplified and sent to a speaker, allowing us to hear the sound.
Different types of pickups, such as single-coil and humbucker pickups, produce distinct tones and are a significant factor in shaping the overall sound of an electric guitar.
Potentiometers and Pickup Selector Switch
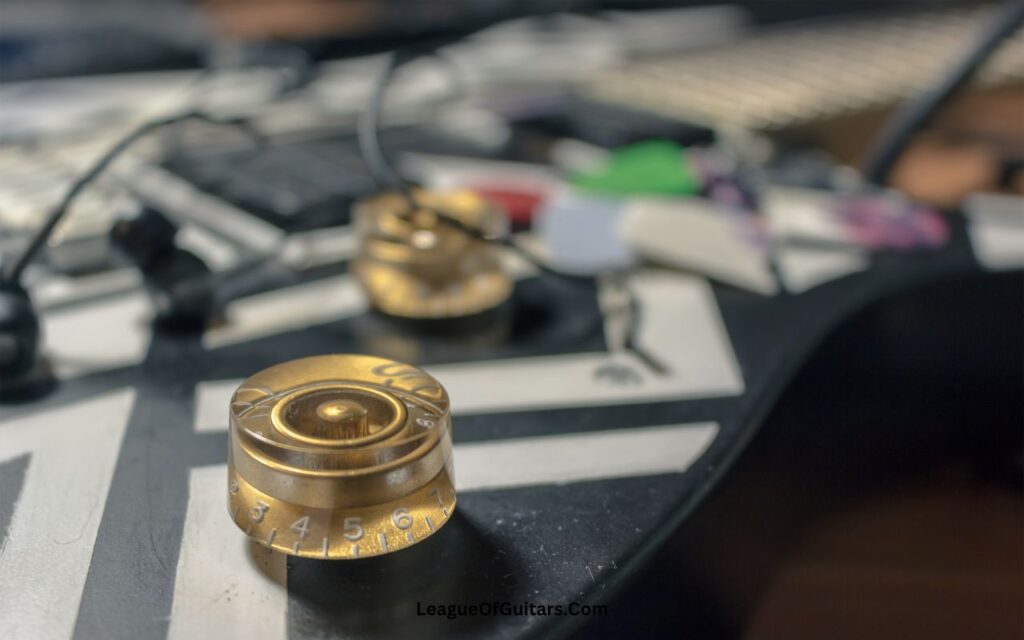

Electric guitars are equipped with potentiometers, which are variable resistors that control the volume and tone of the instrument.
These knobs allow for adjustments in bass, mid-range, and treble frequencies, giving guitarists even more versatility in shaping their sound.
Additionally, electric guitars feature a pickup selector switch, which allows players to choose between different pickups or combinations of pickups, further expanding the range of sounds that can be achieved.

Output Jack
The output jack on an electric guitar is where the cable connecting the guitar to an amplifier is plugged in. It serves as the connection point between the instrument and the amplifier, allowing the electrical signals generated by the pickups to be transferred and amplified.

| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Pickups | Convert string vibrations into electrical signals |
| Potentiometers | Control volume and tone |
| Pickup Selector Switch | Choose different pickups for different sounds |
| Output Jack | Connect the guitar to an amplifier |
| Tone Control Knobs | Allow adjustments in frequency response |
Importance of Guitar Neck and Headstock
Understanding the guitar neck and headstock is essential for both beginners and experienced players.
As you navigate the fretboard, the neck will become your guide, allowing you to explore different chords, scales, and melodies.
Meanwhile, the headstock ensures that your guitar stays in tune and ready to produce beautiful music.
| Feature | Guitar Neck | Guitar Headstock |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Connects the body to the headstock and holds the frets | Houses the tuning pegs for string tension adjustment |
| Material | Typically made of wood | Variety of materials, commonly wood or synthetic materials |
| Components | Frets to navigate and play different notes | Tuning pegs and nut for string tension adjustment |
| Importance | Vital for playing chords, scales, and melodies | Ensures the guitar stays in tune |
We have written a comprehensive guitar buying guide on our blog.
Be sure to read it if you’re interested.
Final Words
So there you have it!
By understanding the anatomy of a guitar and considering factors such as volume, tone, and comfort, you’ll be well-equipped to find the guitar that suits your style and musical aspirations. Happy guitar hunting!
FAQs
Why is it important to learn the names of different parts of the guitar?
Learning the names of different parts of the guitar is essential for beginners. It helps you understand how the instrument works and allows you to communicate with other musicians and guitarists.
How many strings are there on a guitar?
There are six strings on a guitar. Each string is numbered and has a specific name, starting from the thinnest string, commonly referred to as the high E string, through to the thickest string, often called the low E string.
What additional parts do electric guitars have?
Electric guitars have additional parts like pickups, potentiometers, a pickup selector switch, and an input jack. These components are necessary for converting the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals and amplifying the sound.
What are the common parts of a guitar?
All guitars have common parts like the headstock, tuners, tuning pegs, nut, neck, fretboard, frets, body, soundhole, bridge, saddle, and bridge pins. These components work together to create the sound produced by the instrument.
How do acoustic guitars produce sound?
Acoustic guitars have a resonant body that amplifies the vibrations of the strings. The body has a soundhole in the center, which allows the sound to project outward, creating a rich and full acoustic tone.
What is the role of the bridge and saddle on a guitar?
The bridge and saddle hold the strings in place and transmit their vibrations to the body of the guitar. This vibration transfer is crucial for producing sound and resonance.
How do electric guitars produce sound?
Electric guitars use pickups to convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to an amplifier, where they are amplified and projected as sound.
What do potentiometers and pickup selector switches do?
Potentiometers on electric guitars control volume and tone, allowing you to adjust the sound according to your preferences. The pickup selector switch, on the other hand, lets you choose different pickups for different sounds and tones.
What is the purpose of the neck and headstock on a guitar?
The neck connects the body to the headstock and holds the frets. It is where you navigate the strings and play different notes. The headstock, on the other hand, houses the tuning pegs for adjusting the tension of the strings.
Do acoustic guitars need amplifiers?
No, acoustic guitars produce sound through the resonance of their body and do not require amplification. They can be played without the need for additional equipment.
How do I choose the right guitar for me?
When choosing a guitar, consider factors such as volume, tone, and comfort. Acoustic and electric guitars offer different sound options and playing experiences, so it’s essential to try out different models to find the one that suits your preferences and playing style.
How will understanding guitar anatomy help me in selecting a guitar?
Understanding guitar anatomy will help you make an informed decision when selecting a guitar. By knowing the various parts and their functions, you can assess the quality and features of different instruments, ensuring you choose one that meets your musical needs.

2 thoughts on “Guitar Anatomy: Different Parts of a Guitar with Images”